For Structural and Bridge Engineers
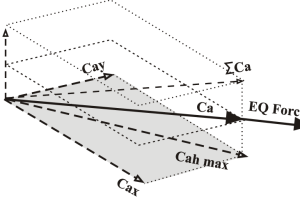
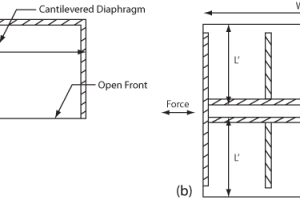
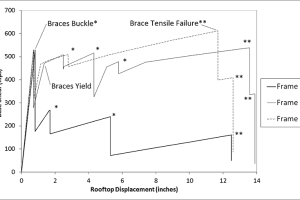
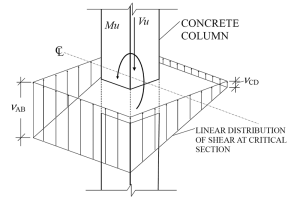
A new method has been developed for measuring the force of ground shaking during earthquakes at particular locations. The proposed Earthquake Shaking Force (EqSF) rating is based on the maximum vector sum of the recorded ground accelerations in the three main directions scaled with the strong ground motion duration. …